Visibly Human Health and Disease in the Human Body
The Musculoskeletal System
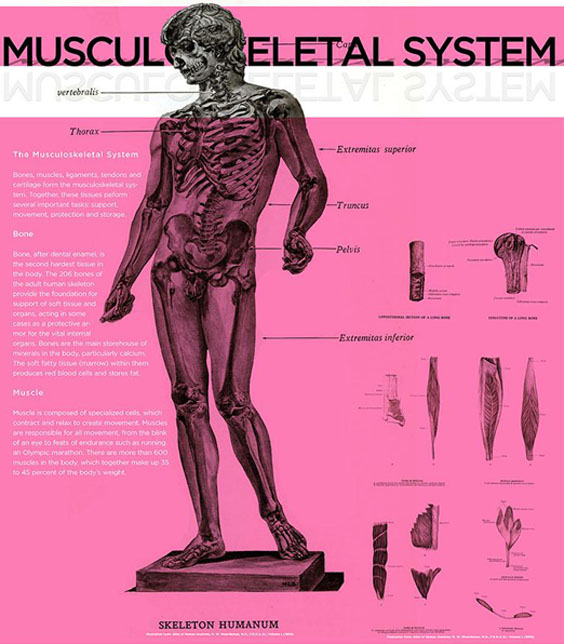 Bones, muscles, ligaments, tendons and cartilage comprise the musculoskeletal system. Together, these tissues perform several important tasks that include support, movement, protection and storage.
Bones, muscles, ligaments, tendons and cartilage comprise the musculoskeletal system. Together, these tissues perform several important tasks that include support, movement, protection and storage.
Bone
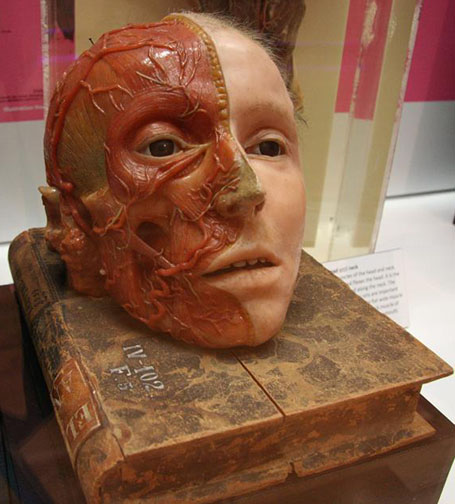
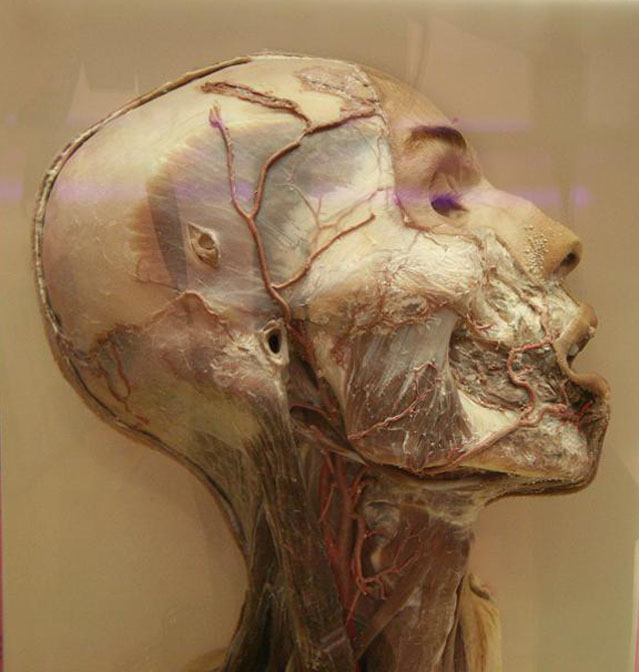
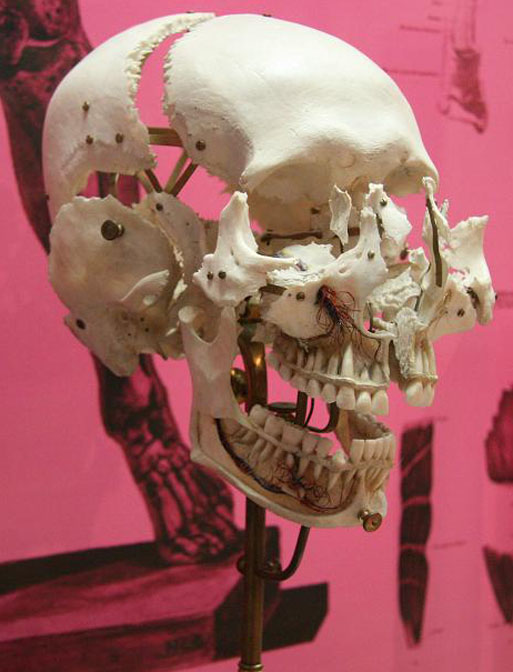
Bone is a living and dynamic tissue. It is composed of an organic phase that gives bone flexibility, while its inorganic phase gives bone its rigidity. After dental enamel, bone is the second hardest tissue in the body. The adult human skeleton consists of 206 bones that provide support of soft tissue and organs, and acts as a protective armor for the vital internal organs. Bones are the main storehouse of minerals in the body, particularly calcium and phosphorus. The soft fatty tissue (marrow) within them produces red blood cells and stores fat.
Muscle
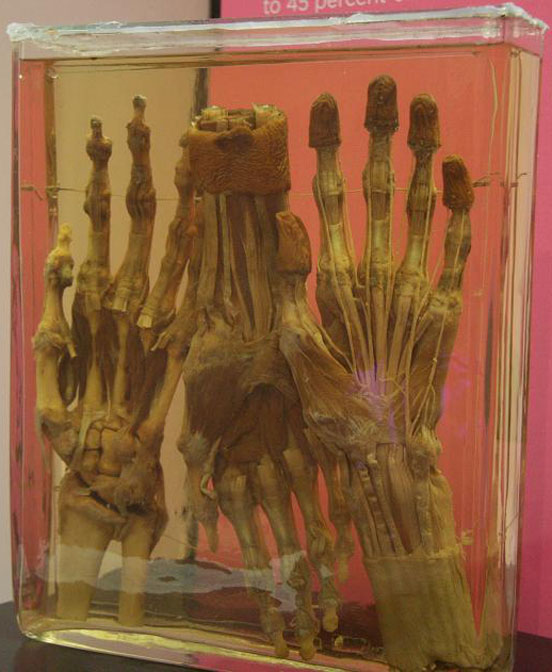
Muscle of the human body comes in three forms: skeletal, smooth and cardiac. Skeletal muscles account for the majority of muscle mass in the body, and are composed of specialized cells called myofibers that contain myosin and actin proteins that work in tandem to contract and relax, thereby creating movement. Muscles are responsible for all movement, from the blink of an eye to feats of endurance such as running an Olympic marathon. There are more than 600 muscles in the body, which together make up 35 to 45 percent of the body’s weight.
Cartilage, Ligaments and Tendons
Chondrocytes (a mature cartilage cell) form three different types of cartilage within the human body: elastic, hyaline, and fibrous. All cartilage is flexible and spongy, and is composed of various concentrations of collagen proteins, elastin and proteoglycins. Hyaline cartilage lines the surface of joints and along with synovial fluid acts as a shock absorber, allowing smooth and fluid movement of the joints. Among other places, fibrous and elastic cartilage can be found in the ears and the tip of the nose.
Ligaments are dense fibrous bands of cartilaginous tissue that hold bones together at various joint surfaces. Ligaments not only increase the stability of joints, but also permit greater flexibility for biomechanical activity, such as throwing a baseball or kicking a soccer ball.
Tendons are strong flexible straps of connective tissue that are similar to ligaments in that they are composed primarily of collagen fibrils. Tendons however, attach muscle to bone and serve as pulley to permit proper muscle flexion, extension, abduction, adduction and rotation.

- Visibly Human Health and Disease in the Human Body
- The Cardiovascular System
- The Urinary System
- Respiratory System
- The Lymphatic System
- The Musculoskeletal System
- The Liver and Hepatic System
- The Digestive System
- The Brain and Nervous System
- Psychiatric Patients at Forest Glen
- Skeleton of Spanish American War Veteran Showing Evidence of Severe Arthritis